Introduction to basics of oracle SQL course
Let's start a brief introduction about the basics of oracle SQL course, which was already revised in the sql basic courses.
In this second part of the basics we going to discuss some important operators, alias name usage and others etc..
Overview to basics of Oracle SQL course
Basic is the root of all interviews and also useful for Oracle certification courses. In this part we cover the below listed topics in basics of oracle SQL course :
- Alias name
- Dual Table (also called as Dummy Table)
- Operators in oracle
- Comment
- What is mean by NULL ?
- Usage of CONCAT ( || )
Brief explanation about the basics of Oracle SQL course
The above listed overview are explained briefly below, so if any doubts means take a screenshot and send to official mail of eduflee.
Alias Name
Alias Name is used to rename the column heading. while we are writing any expression means it will shows in column heading instead we can use alias Name.
WITHOUT ALIAS NAME
WITH ALIAS NAME
Six different ways to use Alias Name
For one word and two word alias name usage
Transaction and Transaction_detail
- Using AS => SELECT debit-credit AS transaction FROM orders;
- Without Using AS => SELECT debit - credit transaction FROM orders;
- Using literal with AS => SELECT debit - credit AS "transaction detail" FROM orders;
- Using literal without AS => SELECT debit - credit "transaction detail" FROM orders;
- Using Underscore => SELECT debit -credit transaction_detail FROM orders;
- Using underscore and literal => SELECT debit -credit "transaction_detail" FROM orders;
Should not use in the below format
- SELECT debit-credit transaction details FROM orders; (gap is there)
- SELECT debit - credit 'transaction details' (double literal should be used)
All the below queries are using in Alias Name only.
Dual Table
- Dual Table is also called as dummy table.
- It is used to process our own data.
- It is used to view the results and functions while doing any calculations.
* mentions all columns, so one row with multiple columns.
Column Name : Dummy
Table Name : Dual
Default Data : X
Owner : SYS
Data Type : Varchar2
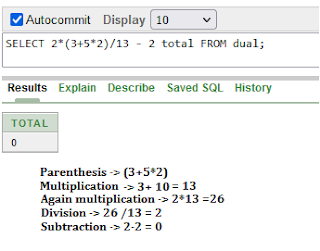
Using dual table for calculation
Operators in Oracle SQL
All the operators in Oracle SQL are used in condition based expression in WHERE clause, HAVING clause.
Arithmetical Operators
PEMDAS => Parenthesis, Exponential, Multiplication, Division, Addition, Subtraction
- IN, NOT IN
- BETWEEN.....AND...
- LIKE, NOT LIKE
- IS NULL, IS NOT NULL
IN operator in Oracle will gives you absolute which means 100% true values only be written as output.
NOT IN operator in Oracle will never be judged when there is 'NULL' values in the particular column means this can be seen detailed in Interview Classes.
BETWEEN.... AND...
It is used to give the ranges between two initial and final points that range condition can be retrived by using BETWEEN..AND..
LIKE The value that are similar to the given condition in LIKE operator as shown in figure, it is used in the case of pattern matching
In Like, if we mention one underscore means it will be mentioning a one character , and % means it will be something or nothing. check in practice solution the figure below.
NOT LIKE It is opposite to LIKE operator it won't give the condition that which are using.
IS NULL It is an operator that can be used only when the condition of that column is in NULL condition so it may shows only NULL records.
IS NOT NULL It is opposite of NULL value.
Practice solution:
Logical Operators
- AND => This is used when both the condition is true
- OR => This is used when any one of the condition is true
- NOT => This is used when that should not be there in the columns. ( < > , != )
In later classes this operators are used in writing queries.
Comment
- Comment is used for back up
- It will makes user friendly to the developers.
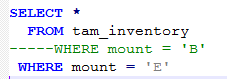
Single Line Comment
In the above image the WHERE mount = 'B' mentioned as an comment. so this can be used at any time. If we remove the ( - ) hyphens then it can be used as an normal query.
Multiple Line Comment
Unknown Value | Unavailable Data | Unassigned Value.
NULL <> Zero
NULL <> SPACE
NULL <> Special Characters
NULL <> NULL
NULL + 20 = NULL
NULL * 20 = NULL
Note: ' < > ' means NOT equal
Usage of CONCAT ( || )
- Concat is used to join only two fields and we can call as pipe operator (||)
- Concat is used to join two or more columns as a output while giving any output or while retrieving data based on the requirement by using two columns which is shown in figure below
To practice the above topic use this below query ... and practice in your own way.
CREATE TABLE eduflee
(id NUMBER,
view_name VARCHAR2(20),
education VARCHAR2(30),
age NUMBER);
----- Paste the above query to your SQL developer tool and after executing paste the below code
BEGIN
INSERT INTO eduflee VALUES (1, 'kaviarasan', 'BE', 30);
INSERT INTO eduflee VALUES (2, 'abirami', 'CA', 35);
INSERT INTO eduflee VALUES (3, 'john', 'HR', 40);
INSERT INTO eduflee VALUES (4, 'ram' 'HR', 30);
INSERT INTO eduflee VALUES (5, 'jana' 'Bcom', 30);
INSERT INTO eduflee VALUES (6, 'zakir' 'Mcom', 40);
INSERT INTO eduflee VALUES (7, 'surya' 'MBA', 60);
INSERT INTO eduflee VALUES (8, 'sachin' 'sslc', 50);
COMMIT;END;
/
By using this you can able to retrieve data.
CONCLUSION
I hope you are enjoyed this part, but its little tough to understand in the beginning, but if you keep on practicing this basics means it will be easy to learn other part of the course.
So, If you having any doubts or queries related to this session means kindly comment below.
Practice session
Note: Use Eduflee Table by running the above query.
1, Write to a query to fetch only id and view_name as name in the eduflee table.
2, Write a query to calculate 40+60*3-30 ?
3, Write a query to find the view_name should starts with 's' ?
4, Write a query to find age of the viewers between 50 and 60 in eduflee table
5, Write a query to find the education to be 'sslc' in eduflee table
6, Write a query to find the education should not be 'HR' and 'sslc'











Clear for understanding, the image itself helpful for me to understand the concept better
ReplyDelete