Functions in Oracle SQL
Functions is one of the important features in Oracle SQL, with the help of this functions we can able to get the result as per our requirement.
Functions in Oracle SQL contains Single Row Functions, Multiple Row Functions.
Mainly those functions are used to returns value based on the input that which we given. And practicing this functions in oracle SQL, one can able to master in query writing.
Functions is used to perform some actions like doing any calculations, grouping the data, conversion in type, date conversion etc.
Types of Functions in Oracle SQL
Functions in oracle is classified on the basis of the input which we are giving and getting the output, and they are:
- Single Row Functions
- Multiple Row Functions
Single Row Functions in Oracle SQL
Single Row Functions works on the single rows which will shows the result for that single rows only.
If "n" number of inputs to give "n" number of outputs.
From the above figure explains about the single row functions, in that length is the type of single row functions so for every input it will gives one outputs.
Let we discuss what are the functions that are under Single Row functions.
This single row functions contains some divisions such as:
- Character Functions
- Number Functions
- Date Functions
- Type Functions
- General Functions / Null Functions
Character Functions
Character Functions is used to return any of the value it may be a variable or numbers. For every input it will gives an output. And this character functions can be manipulated by two methods: They are Case manipulation and Character manipulation
Case Manipulation
UPPER ( ) LOWER ( ) INITCAP ( )
Character Manipulation
LENGTH( ) REVERSE ( )
CONCAT ( )
SUBSTR ( ) INSTR ( )
LPAD ( ) RPAD ( )
LTRIM ( ) RTRIM ( )
REPLACE ( ) TRANSLATE ( )
UPPER ( ) LOWER ( ) INITCAP ( )
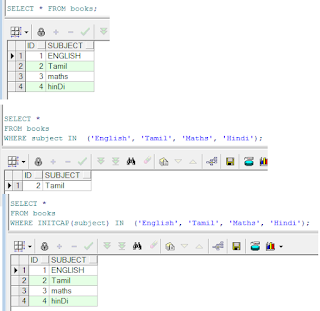
- The UPPER ( ) , LOWER () and INITCAP () Keyword is used to retrieve the data in the form of UPPER, LOWER, INITCAP case.
Example:
- This case manipulation is used to retrieve the data from the table, based on the input that we given in the conditions.
Example:
LENGTH ()
Length is used to measure the size of any variable or number.
Example:
It will calculates the space also.
Try it by Yourself
- Calculate the length of the null value.
- Calculate the length of the number
- Calculate the length of the number (000000753)
CONCAT ( )
Concatenation is a function is used to join two characters or numbers. It is similar to pipe operator ( || )
Note: This function will contain only two arguments, if we need to join more than two string or variable means we need to add another concat.
This both results gives same output.
- Concatenate two or three variables
- 77777, eduflee concat both the numbers and variables.
REVERSE ( )
Reverse function in oracle sql is one of the easiest function is used to reverse the variables.
For example
SELECT REVERSE ('abcdefgh') FROM dual;
Output:
hgfedcba
SUBSTR AND INSTR ( Substring and Instring)
#Substring and Instring is the most important functions which are mostly used while quering.
SUBSTR => Using this function we can get the part of the variables or numbers.
For example
EDUFLEE -> Print first three character in this word.
Output : EDU
To get the part of the string below arguments to be followed:
Syntax : SUBSTR ( input_string, Starting_position, No_of_characters_to_be_printed )
Input_string => here you can place a column name or the required variables or numbers
Starting_postion => It should be number
No_of_characters_to_be_printed => It should be also a number.
From the above example the word : EDUFLEE can be substring to get the particular part as EDU.
So input string => Eduflee, Starting position => 1, No of characters to be printed => 3
Try it yourself
- Print first 4 letters from the word 'ORACLE'
- Print the particular word "possible" from this word 'IMPOSSIBLE'
INSTR => Using this function we can identify the position of the particular character.
For example
EDUFLEE -> Print the position of the letter 'U'
Output : 3
To get the part of the string below arguments to be followed:
Syntax : INSTR ( input_string, particular character)
2 Arguments are mandatory and other 2 is optionally used based on the requirements.
Input_string => here you can place a column name or the required variables or numbers
Particular character => it can be two letter word or single letter can be used.
optional arguments
Starting_position => It should be number
Position of the character => It should be also a number.
From the above example the word : Eduflee contains many 'E', to check the position of each letter we used instring .
So input string => Eduflee,
Particular character will be 'E',
Starting position ,
position of 'E' from this starting position.
INSTR ('EDUFLEE', 'E', 1, 2) => From the 1st position, it will checks the position of 2nd 'E' in the result set. so output will be 6
INSTR ('EDUFLEE', 'E', 3, 1) => From the 3rd position (U is the 3rd letter), it will checks the position of 1st 'E' in the result set so output will be 6
In the same way try the below query to know more.
SELECT INSTR ('EDUFLEE', 'E', 1, 1) output1,
INSTR ('EDUFLEE', 'E', 1, 2) output2,
INSTR ('EDUFLEE', 'E', 1, 3) output3,
INSTR ('EDUFLEE', 'E', 2, 1) output4,
INSTR ('EDUFLEE', 'E', 2, 2) output5,
INSTR ('EDUFLEE', 'E', 3, 1) output6 FROM dual;
Try it yourself
- Find the position of ' 2nd ' I ' in the word 'INDIA' => Use 4 arguments
- Find the position of particular word "possible" from this word 'IMPOSSIBLE'
LPAD and RPAD
Normally, we use padding to add additional spaces in the borders especially in CSS we can able to see those details.
In SQL, padding is used to create extra spaces or characters to be printed in front or beside of the given input.
From the below example we can able to see that this account number column is padded in front and beside.
- Mask the account number from 32140056374 into 32XXXXXXX74
LTRIM and RTRIM
TRIM is exactly opposite to padding, where in padding we added the characters but in TRIM we are removing the characters.
TRIM is used to cut the similar characters in left or right side of the particular input which user is given.
LTRIM is used to remove the similar characters in the left side of the input.
RTRIM is used to remove the similar characters in the right side of the input.
For example:
LTRIM () RTRIM() TRIM() ----Default it will cut spaces on both sides.
LTRIM is used to cut the left side similar characters
Try the below query for more understanding in this concepts.
SELECT '00000000000986586851200' data
,LTRIM ('00000000000986586851200', '0')
FROM dual;
SELECT '00000000000986586851200' data
,RTRIM ('00000000000986586851200', '0')
FROM dual;
SELECT '00000000000986586851200' data
,LTRIM ('00000000000986586851200', '0')"LTRIM"
,RTRIM ('00000000000986586851200', '0')"RTRIM"
,LTRIM (RTRIM ('00000000000986586851200', '0'),'0')"TRIM"
FROM dual;
SELECT '00000000000986586851200' data
,TRIM ('0' FROM '00000000000986586851200')"TRIM"
FROM dual;
REPLACE and TRANSLATE
Replace and translate is used to change the input based on the requirements that which was given in the arguments.
It contains three arguments,
Argument 1 => Input
Argument 2 => characters that requires changes.
Argument 3 => characters that to be placed in the input.
Replace is the function used to replace the exact characters is present in the inputs. From the below image we can able to see that the character lc is completely replaced to xy, but the replacement will not be possible if the character is cl
Translate is the function also used to replace the characters present in the inputs. But here it will not check the exact match for that input string. From the below output shows that the letter l is replaced to x and letter c is replaced to y
For the below example:
Argument 1 => 'Welcome to oracle'
Argument 2 => 'lc'
Argument 3 => 'xy'












Comments
Post a Comment
Thanks for commenting, we will always respond your comment.